【文献阅读】P-Tuning v2: Prompt Tuning Can Be Comparable to Fine-tuning Universally Across Scales and Tasks
机构:清华
论文地址:
论文代码:
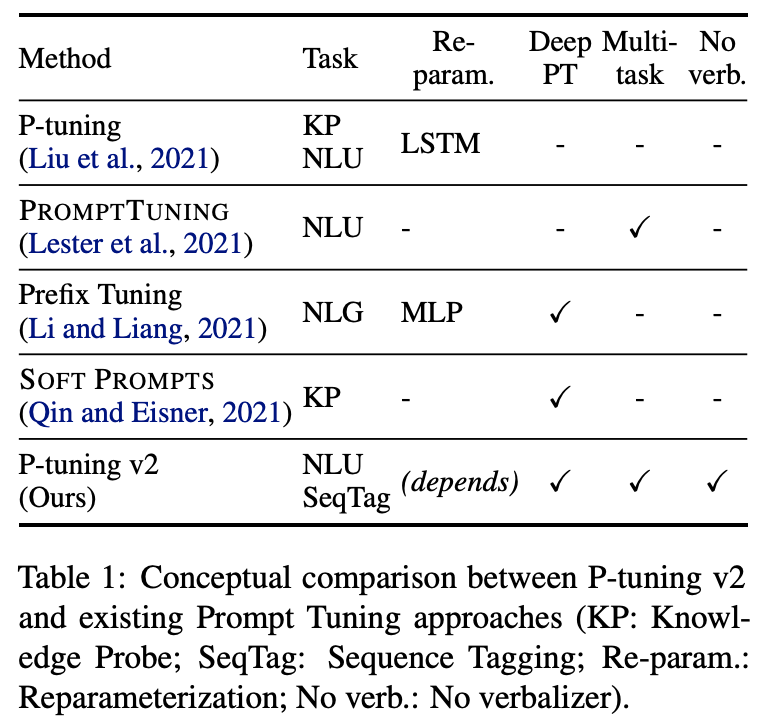
介绍
P-Tuning仅对大模型的Embedding加入新的参数。
P-Tuning v2,在大模型的Embedding和每一层layer前都加上新的参数。
模型
P-tuning存在以下两个缺陷:
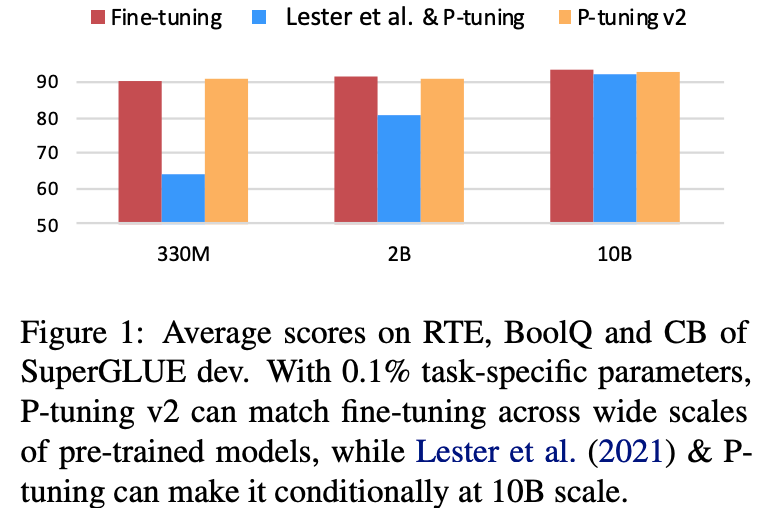
Lack of universality across scales: 对于参数数量在10B以下的模型,p-tuning表现的比fine-tuning要差很多。Lack of universality across tasks: 对于分类问题,p-tuning可以表现的较好,但是对于序列标注这种hard sequence tagging tasks,p-tuning表现的较差。
针对上述问题,作者提出了P-Tuning v2。 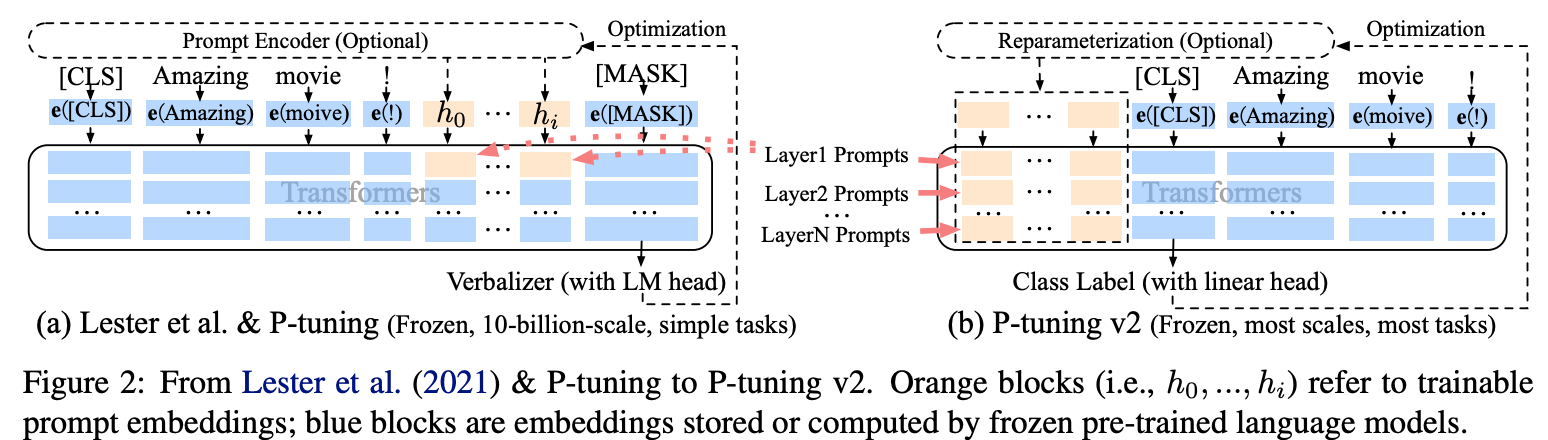
如上图所示,在P-tuning中,continuous prompts只在embedding层插入。而在P-tuning
v2中,continuous prompts在每一个layer层都可以作为prefix tokens被插入。这样可以带来两个好处:
- P-tuning v2拥有更多的可学习参数,可以在微调的时候学到更多的东西。
- 在更深层中加入的
continuous prompts可以更好的影响模型的输出。
其他细节和结果
Reparameterization
P-tuning中使用了双向的LSTM对continuous prompts进行编码,在P-tuning
v2中发现这一改进在有些任务中会带来积极作用,但在有些任务中会带来消极作用。
Prompt Length
We find that different NLU tasks usually achieve their best performance with different prompt lengths. Generally, simple classification tasks prefer shorter prompts (less than 20); hard sequence labeling tasks prefer longer ones (around 100).
Multi-task Learning
可以通过多任务训练共享的continuous prompts来对其进行更好的初始化,然后再在特定的下游任务中对continuous prompts进行微调。
结果和对比